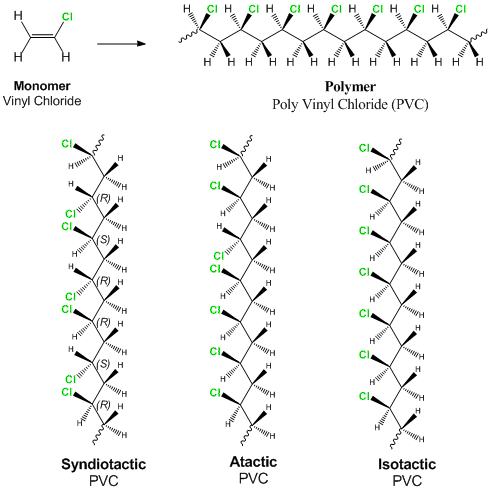
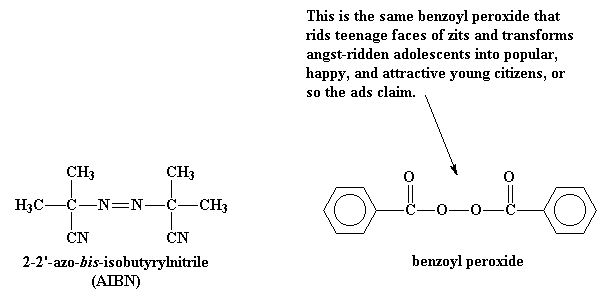
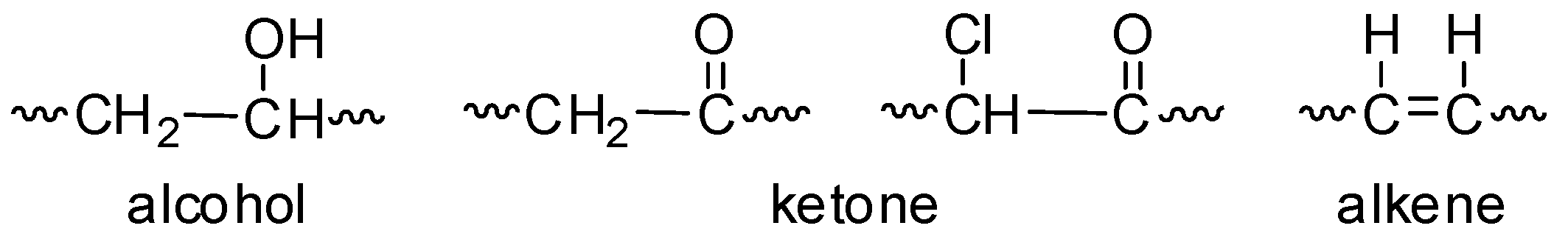
Poly Vinyl Chloride Chain Transfer Mechanism
This polymerisation reaction proceeds by a free radical mechanism.
Poly vinyl chloride chain transfer mechanism. Determination of short chain branches in poly vinyl chloride and ethylene vinyl chloride copolymers by pyrolysis hydrogenation gas chromatography. The procedure to take samples at different periods of time has been described previously coelho 2006 as have the reaction mechanism features coelho et al 2011 percec et al 2004a fig. Polymerization conversion of monomers join in a chain to form polymers process is called polymerization monomer mono single mer unit the reactant species in polymerization process called as monomers. Shuncong mao hajime ohtani shin tsuge hiroshi niwa masatoshi nagata.
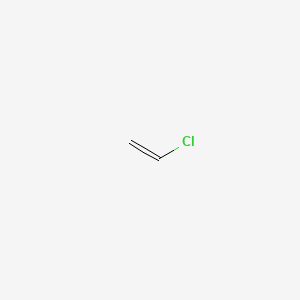
1 shows the comparison between the molecular weight evolution vs time for. Chain transfer reactions are especially prevalent in the high pressure radical polymerization of ethylene which is the method used to make ldpe low density polyethylene. Poly vinyl chloride pvc as a significant practical and salable polymer has been extensively studied because of its excellent film forming and favorable properties such as workability chemical. Polyvinyl chloride is a white rigid quite brittle solid.
Polymers joining of monomers to form big molecules called as polymers these are high in molecular weight molecules. Isopropyl chloride 2 4 dichloropentane and 2 4 6 trichloroheptane were used as solvents. The 1º radical at the end of a growing chain is converted to a more stable 2º radical by hydrogen atom transfer. The most important technological procedure in the production of pvc is the suspension polymerization of vinyl chloride as processibility of the polymer may be influenced to a considerable extent by the choice of polymerization conditions.
Physical constants of poly vinyl chloride. Comments on recent studies w h. Chain transfer and control of molecular weight are mediated by the activation energy of head to head addition and thus by polymerization temperature alone. Addition of vcm to growing pvc chain.
The participation of chain transfer reactions in the polymerization of vinyl chloride in solutions has been elucidated. The molecular weight profile of the set dtlrp of vcm was determined for different operational conditions in the 150 l reactor. Polyvinyl chloride is produced in an addition polymerisation reaction using the chloroethene vinyl chloride monomer. Additives are used to modify the properties of polyvinyl chloride to make it more useful.
Pvc is the only major commercial polymer wherein polymerization temperature controls molecular weight and molecular weight distribution. Box 8795 williamsburg va 23187 8795 usa abstract investigations in the title areas within the past ten years are summarized and critiqued.