Identification Larvae Carpet Moths

These pests look similar at the larval stage.
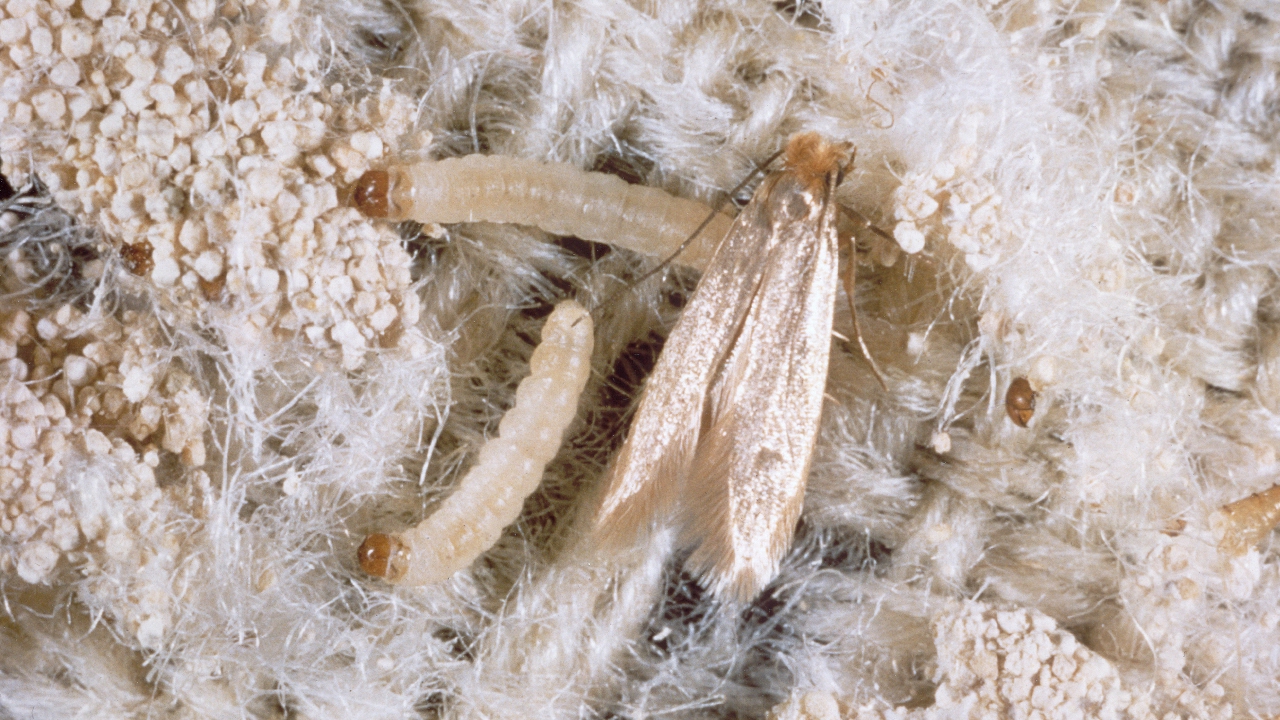
Identification larvae carpet moths. Identify webbing clothes moth larvae by their feeding tunnels of silk or webbing patches left behind on the fabric as they move around. Adult webbing clothes moths have a wingspread of about 1 2 inch and that of the male is somewhat less. Carpet tapestry moths tend to lay their eggs in the darkest patches of your carpet such as under furniture behind curtains or by skirting boards. Carpet moth eggs are so small you won t notice them but their larvae are easily identified due to the case they carry around which gives them their common name.
As the larvae grow they leave empty hairy cast skins or husks which are often the first sign of carpet beetle attack figure 7. With a body about 5mm long and a wingspan of about 14 18mm. Regular vacuuming in these areas moving furniture and opening curtains. It is the larvae that eat your carpets not the adult moths.
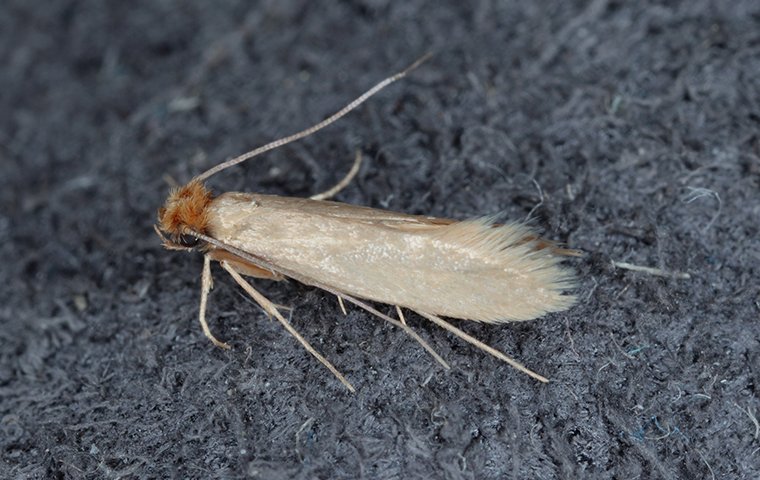
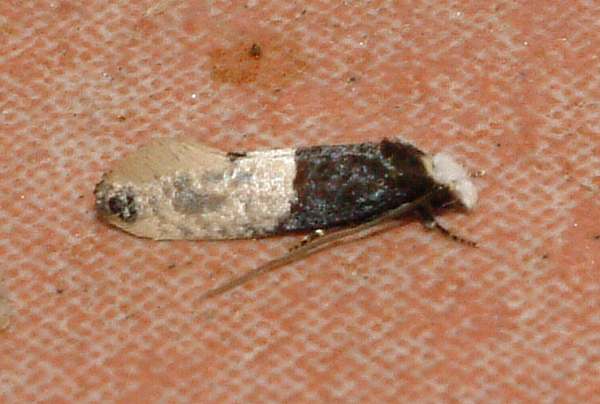
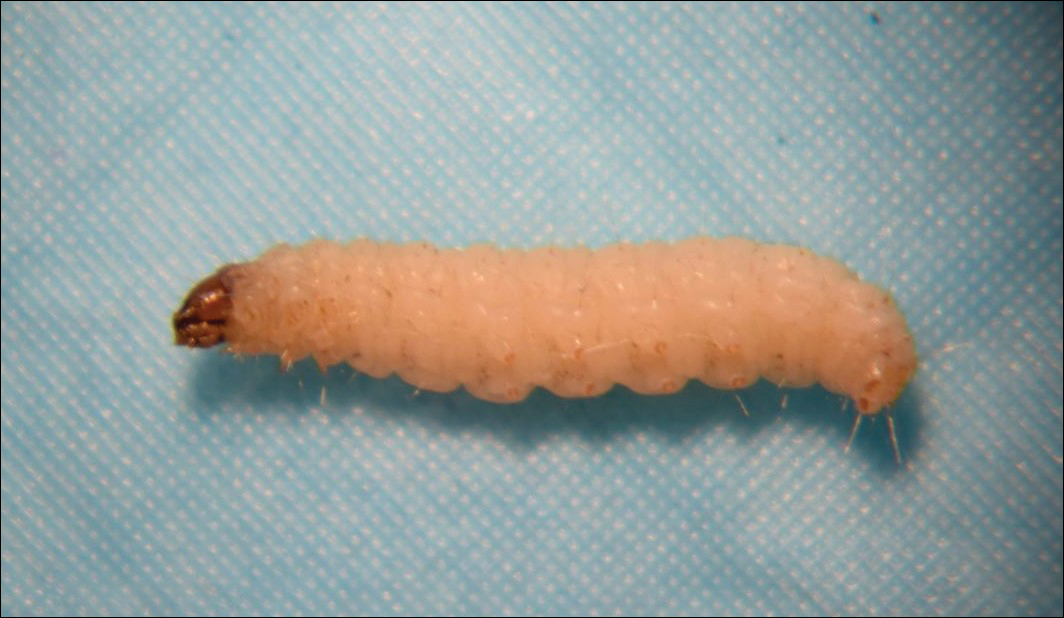
Identifying a carpet moth the carpet moth is smaller than a common house moth. The larvae are creamy white coloured caterpillars which can be as much as a 1 2 inch in length. Identifying clothes moths the most common clothes moths are the webbing clothes moth easily identified with a golden color and around half an inch in length and the case bearing moth which can be identified about inch long and their forewings are mottled brown with one large and a few smaller indistinct black spots. The larvae are white with a brown head.
If you spot a tiny grub wrapped in a woven case dragging itself around you ve got carpet moths. Identifying moth larvae the two most common moth species in the mid atlantic are clothes moths and meal moths. Adults lay cream coloured eggs which hatch into creamy white larvae. A broad winged green moth with dark blotches and wavy white lines across the wings.
Carpet moths are buff coloured with forewings that usually have three distinct dots. Figure 7 cast skins of varied carpet beetle larvae the larvae will grow to 5mm long and are voracious feeders which will rapidly make holes in woollen textiles animal specimens fur and feathers. Carpet moths inhabit less disturbed and darker areas behind sofas along skirting boards under bookcases are typical hiding places for carpet moth larvae. Case bearing clothes moth larvae create smaller more regular shaped holes in garments and textiles.
Common clothes moth larvae cause irregular shaped holes in natural fabrics.